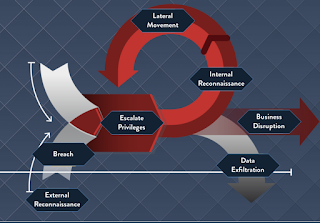
Not to be outdone Alabama is the final state to pass a Data Protection Bill
Right on the heels of South Dakota, who passed their data protection bill in February of this year, Alabama is the 50th and final State to pass a data protection bill. Alabama SB 318 was passed this month. The codification of state data protection laws began in 2003 with California. To date all remaining states have followed suit. SB 318 , seemingly incorporates Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act's ( HIPAA ) terminology and some application. Class of protected The statute applies to individuals residing within the state. Individuals rights Individuals are afforded protection from the breach , which is defined as the unauthorized acquisition of personally identifiable information (PII). PII is also referred to as personal data , in some jurisdictions. Data Protected The statute outlines the type of PII that is protected under the statute as “electronic data ” that can be any of the following : Identification number (military, driver’s...